· energy efficient home upgrades · 5 min read
What's a Heat Pump?
Rediscover heat pumps, an age-old technology that has been modernized to provide both heating and cooling solutions for your home.

A heat pump is a versatile climate control system that can both heat and cool your home. It operates on the simple yet effective principle of heat transfer. Just like a refrigerator uses refrigerant to extract heat from its interior and keep your food cool, a heat pump extracts heat from one location and transfers it to another. During the winter, it pulls heat from the outdoor air or ground and moves it inside your home for warmth. In the summer, the process reverses: it extracts heat from your home’s interior and expels it outside to keep your living space cool. This dual functionality makes heat pumps an incredibly versatile solution for home heating and cooling, offering year-round comfort.
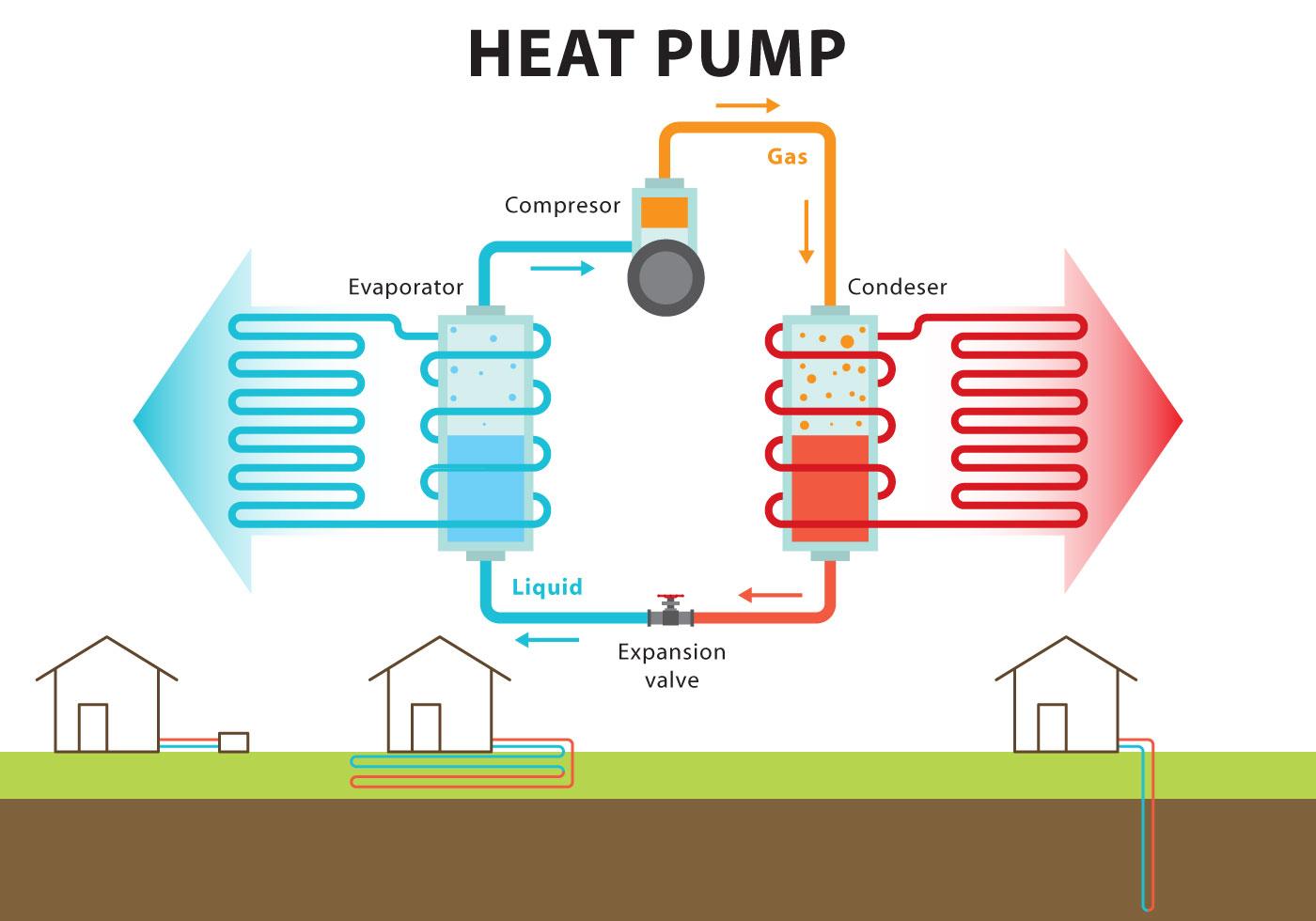
A Closer Look at The Components of a Heat Pump
A heat pump isn’t just a piece of machinery; it’s a marvel of modern engineering that operates similarly to a refrigerator. It consists of several key components that work in harmony to transfer heat efficiently:
Evaporator: This is where the magic starts. The evaporator absorbs heat from the source—either the outside air or ground—much like a refrigerator’s evaporator absorbs heat from the food.
Compressor: Often referred to as the heart of the heat pump, the compressor pressurizes the refrigerant gas, elevating its temperature and pressure. This prepares the refrigerant for the heat transfer process.
Condenser: This component releases the absorbed heat to the desired location—either inside your home for heating or outside for cooling.
Expansion Valve: This valve regulates the flow of refrigerant between the high-pressure condenser and the low-pressure evaporator, allowing the refrigerant to cool and expand, readying it for another cycle of heat absorption.
New School Efficiency with Old School Technology
Modern heat pumps are a testament to technological advancement, renowned for their energy efficiency. They are designed to transfer up to three times more energy than they consume, making them a highly efficient alternative to traditional heating systems. This efficiency is further enhanced by advanced features like thermostatic expansion valves for precise control of refrigerant flow and variable-speed blowers that adjust according to your home’s heating or cooling needs. For those on a budget, hybrid heat pump systems offer a more affordable option without significantly sacrificing efficiency.
Air Source Heat Pumps: Capturing the Invisible Heat
Air source heat pumps are the most prevalent type of heat pump and have a significant role in the Inflation Reduction Act. They are covered under both the Electrification Rebate Act and the Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit (25C), which offers up to 30% in tax credits, capped at $600 for ENERGY STAR models with a UEF greater than 0.95. This makes them an attractive option for homeowners looking to benefit from energy-saving incentives.
These heat pumps work by extracting heat from the outdoor air and transferring it inside your home during the winter months. Conversely, in the summer, they reverse the process, removing heat from your home and releasing it outdoors. Their inclusion in these legislative acts highlights their critical role in promoting energy efficiency and reducing costs for homeowners.
Types of Air Source Heat Pumps:
Most Popular: Ducted Split Systems These systems are designed to heat and cool an entire home. They use ductwork to distribute conditioned air throughout the home, making them ideal for larger residences.
Great for the Right Situation: Ductless Mini-Split Systems These systems are perfect for heating and cooling individual rooms. They consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units that deliver air directly into the room, offering more localized control.
Less Common: Ducted Packaged Systems These are all-in-one systems that house the compressor, condenser, and evaporator in a single unit. Typically installed outside, they deliver air through ductwork and are less commonly used due to their bulkier size.
For more information on Air Source heat pumps, check out our Breakdown.
Geothermal Heat Pumps: Tapping into Earth’s Core
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground-source heat pumps, come with a higher initial investment due to the need for underground loop installation. However, they offer several long-term benefits that make them a financially sound choice. They are recognized as a clean energy technology under Section 25D, making homeowners eligible for an uncapped 30% federal tax credit. This means there’s no upper limit to the amount you can claim, providing substantial financial relief.
Types of Geothermal Heat Pumps:
Most Common: Closed-Loop Systems These systems circulate a heat transfer fluid through a loop of pipes buried underground. The fluid absorbs heat from the earth and carries it to the heat pump, making it highly efficient.
Great for the Right Situation: Open-Loop Systems These systems use groundwater from a well as a direct energy source. After transferring its heat to the heat pump, the water is returned to the ground, making it a sustainable option.
Less Common: Pond-Based Systems These systems utilize a nearby pond or lake as a heat source. A loop of pipe is placed at the bottom of the water body, making it an option for homes located near such water sources.
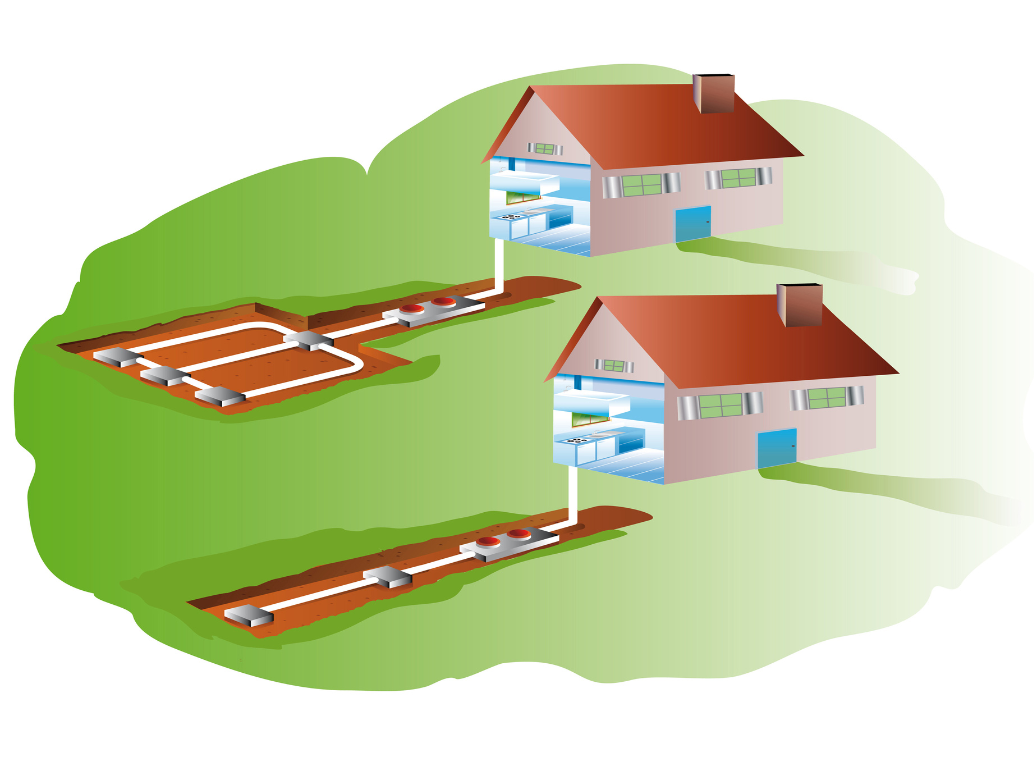
These systems are highly efficient and can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. With proper maintenance, they can last up to 50 years, far outlasting most traditional heating systems that last 10-15 years, thereby enhancing their long-term value.
You can learn more about geothermal heat pumps in this comprehensive guide.
Conclusion
Heat pumps are not just a modern marvel but a sustainable choice for your home’s heating and cooling needs. With dual functionality and high energy efficiency, they offer a year-round comfort solution. Moreover, their inclusion in the Inflation Reduction Act and various tax credits make them a financially viable option. As we transition to a more energy-efficient future, heat pumps stand as a testament to innovation and sustainability.